这道题目的前置知识,曼哈顿距离,即为:$|x_1 - x_2| + |y_1 - y_2|$。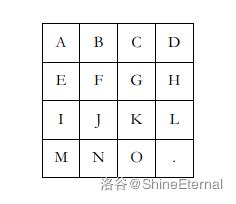
这是原来字母的标准位置,我们可以用一个结构体储存这几个字母的坐标,下标从 $0$ 开始。
1 | struct letter |
接下去是输入,用两层循环 for(int i = 1;i <= 4;i++) 与 for(int j = 1;j <= 4;j++),$i$ 和 $j$ 正好表示输入的字母的坐标。我们现在要求的是所有字母从当前位置到自己的标准位置的曼哈顿距离之和,因此输入的.不需要被计算。那么这样只需要把 $i$ 与 $j$ 分别与该字母的标准进行比较求和就可以了。(注意:$\texttt{A}$ 的 $\text{ASCII}$ 的值等于 $65$,标准的下标从 $0$ 开始)
1 |
|